What is a CONFIG file?
A CONFIG file is known as configuration file; used to configure the parameters and primary settings for several computer softwares. The config File format is used for server processes, software applications, and operating system settings. Some softwares only read their configuration files at their startup. Others check the configuration files for changes periodically. A programmer can write code to instruct a software to read the configuration files again and again after certain time of period and apply the changes to the current process. There are no definitive standards or strong conventions for CONFIG file sysntax. For example, Microsoft’s Web.config file is belongs to CONFIG file format, which consists of an XML based tagsets; can be edited with Microsoft Visual Studio or any other text editor.
Examples of configuration files:
SSH CONFIG file example. OpenSSH client-side configuration file is named CONFIG, and it is stored in the.ssh directory. The SSH CONFIG file consists of the following structure: Host hostname1 SSHOPTION value SSHOPTION value Host hostname2 SSHOPTION value Host. SSHOPTION value Python CONFIG file example.
So I typically run this command a lot: ssh -L 5901:myUser@computer.myHost.edu:5901. I use it to do VNC over SSH. How do I convert that command into something that will work in a /.ssh/config file? Ex: host yam HostName yam.myHost.edu User myUserName. All I want to do is type: ssh yam. And have it open a SSH shell with a local listen port, and a remote port forwarded to it. The OpenSSH server reads a configuration file when it is started. Usually this file is /etc/ssh/sshdconfig, but the location can be changed using the -f command line option when starting sshd. Some organizations run multiple SSH servers at different port numbers, specifying a different configuration file for each server using this option. SSH configuration is generally found in /etc/ssh/sshdconfig. Change SSH Port. We can change the port users use to login away from port 22. Sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshdconfig. Change the Port option to something other than 22: # Formally 'Port 22' Port 2222. Then restart SSH: sudo service ssh restart. Ssh (1) obtains configuration data from the following sources in the following order: 1. Command-line options 2. User's configuration file (/.ssh/config) 3. System-wide configuration file (/etc/ssh/sshconfig) For each parameter, the first obtained value will be used.
Since, the configuration files are not created by following any rules, standrads or conventions, these files might have written by using different formats. A .config file might be based on XML, JSON or any other format. Following are the examples of configuration files for well known operating systems and softwares:
Configuration files in Linux
Every Linux program is an executable file keeping the list of opcodes the CPU executes to accomplish typical operations. The operations of almost every program can be customized to your requirements by changing its configuration files. Several configuration files in the Linux system are in the /etc directory. The configuration files can be classified into the following categories:|Category|Example| Comments|—|—|—||Access files|/etc/host.conf|Tells the network domain server how to look up hostnames.||Booting and login/logout|/etc/rc.d/rc.local|Not official. May be called from rc, rc.sysinit, or /etc/inittab.||File system|/etc/mtools.conf|Configuration for all the operations (mkdir, copy, format, etc.) on a DOS-type filesystem.||System administration|/etc/shells|Holds the list of possible “shells” available to the system.||Networking|/etc/gated.conf|Configuration for gated. Used only by the gated daemon.||System commands|/etc/logrotate.conf|Configuration for the Dynamic Linker.||Daemons|/etc/httpd.conf|The configuration file for Apache, the Web server. This file is typically not in /etc.||User programs| /etc/lynx.cfg| Proxy settings|
Ssh Config Username
AWS CONFIG file example
The frequently used configuration settings and credentials can be saved in CONFIG files that are maintained by the AWS CLI. The CONFIG file must be a plaintext file that uses the following format:
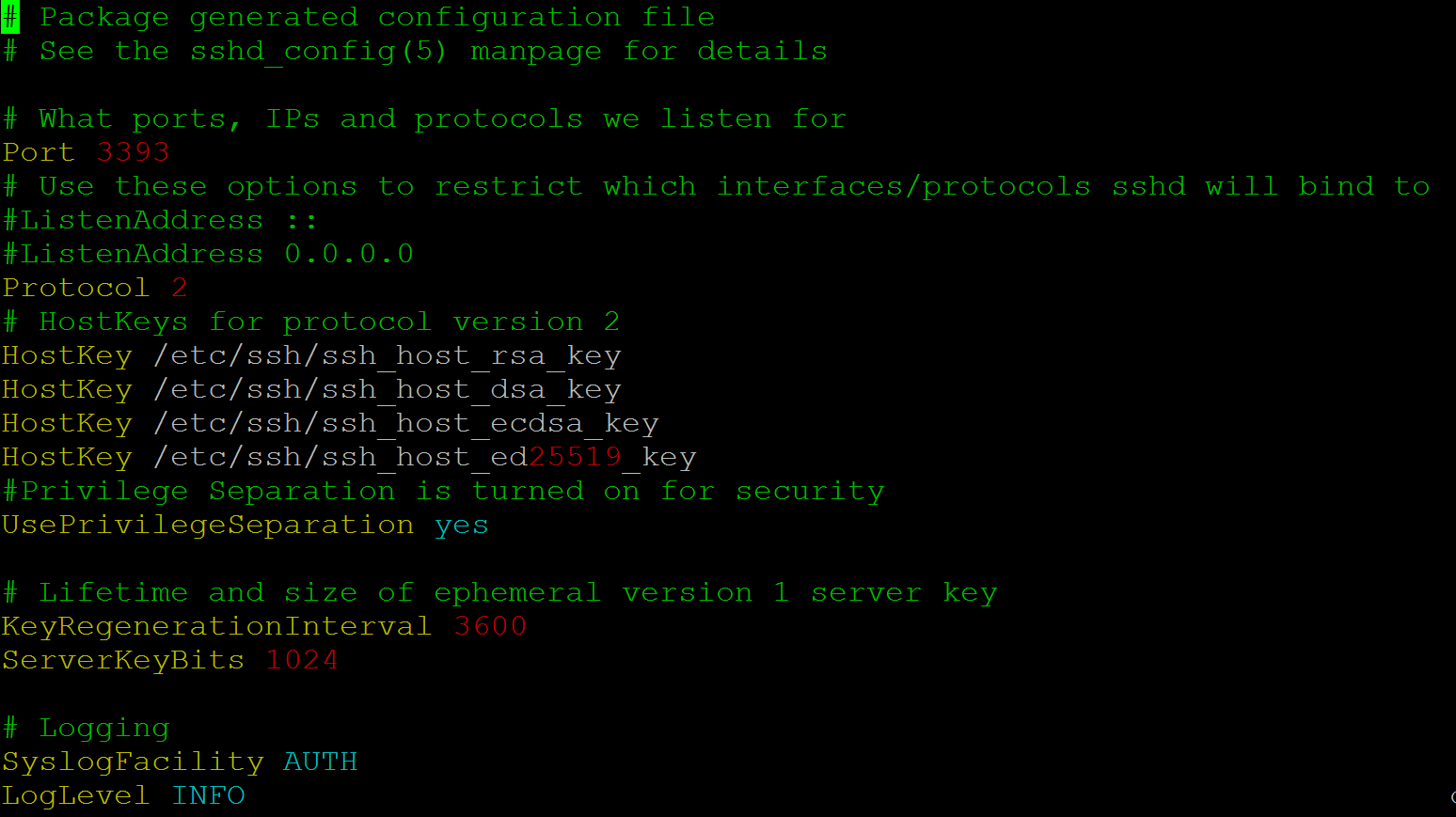
SSH CONFIG file example
OpenSSH client-side configuration file is named CONFIG, and it is stored in the .ssh directory. The SSH CONFIG file consists of the following structure:
Python CONFIG file example

A Python CONFIG file could look like this:
Softwares that can open the CONFIG files
The CONFIG files can be opened in the following softwares:
Ssh Config Keyfile
| Operating System | Software |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows | Microsoft Visual Studio 2019, File Viewer Plus, Adobe Dreamweaver 2020, Microsoft Notepad, Microsoft WordPad |
| MacOS | Adobe Dreamweaver 2020, Apple TextEdit, MacroMates TextMate |
References
Ssh Config File Port Number

Ssh Config File Port Forward
See Also
